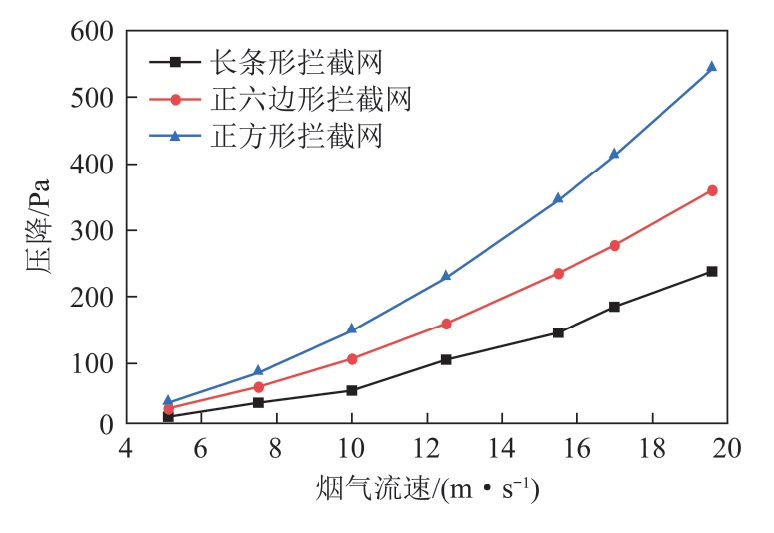
The large ash particles in the flue gas from coal combustion would lead to severe blockage and wear problems of the catalyst in a selective catalytic reduction (SCR)denitrification system,which affects the service life and denitration performance of SCR catalyst. This problem can be effectively solved by installing an interception net device in the flue to intercept large particle ash. The design of interceptor mainly depends on experimental measurement and engineering experience,which lacks general design criteria and theoretical basis,and the research on influence factors of pressure drop is not deeply explored. It is of significance for developing an effective and low-cost interceptor to calculate accurately the pressure drop of the flow across the interceptor with different pore structures. The influences of pore structure,flue gas velocity,interceptor porosity and thickness on the pressure drop were investigated based on computational fluid dynamics by construct the calculation model of interceptor mesh. The simulation results show that controlling parameters on pressure drop are the flow velocity and the porosity. The pressure drop is a quadratic power function of the flow velocity within the range of 5-20 m/s and inversely proportional to the third power of the porosity when the porosity of the interception network is 40%-65%. It is also found that,given the same porosity,the pore structure has negligible effect on the pressure drop. And the strip interceptor has the minimum pressure drop under the condition of the same critical size. The pressure drop increases quasi-linearly with the thickness of interceptor increase in the range 6-18 mm. Based on a large number of simulation data,A correlation is then proposed to predict the pressure drop and the empirical expression of the equivalent porous medium permeability of the interception network is further deduced,which can be feasibly applied to full-scale CFD simulation of SCR denitrification system.
Pressure drop characteristics of large particle ash interceptor in SCR flue gas denitrification system
 2022 No. 06
2022 No. 06
 568
568 298
298

Authors:
- MENG Lei
- LEI Yu
- CHEN Sheng
- LIU Xiaowei
- YUE Pujie
- GU Xiaobing

Unit:
- Datang Environment Industry Group Co.,Ltd.,;State Key Laboratory of Coal Combustion,Huazhong University of Science and Technology

Abstract:

Keywords:
- selective catalytic reduction
- large particle ash
- interceptor
- CFD simulation
- permeability

Citation format:
孟磊(1985—),男,山西定襄人,高级工程师,博士。E-mail:mengl@dteg.com.cn
通讯作者:陈晟(1992—),男,浙江杭州人,副研究员,博士。E-mail:sheng_chen@hust.edu.cn
通讯作者:陈晟(1992—),男,浙江杭州人,副研究员,博士。E-mail:sheng_chen@hust.edu.cn

Chart:

Articles:
--

Citation format:
--

-
Executive director
China Coal Science and Industry Group Co., Ltd
-
Sponsored by
Coal Science Research Institute Co., Ltd
Coal Industry Clean Coal Engineering
Technology Research Center -
Editor in Chief
XIE Qiang
-
Vice Editor-in-Chief
YU Chang
SHI Yixiang
ZHAO Yongchun
DUAN Linbo
CAO Jingpei
ZENG Jie -
Publication Frequencies
Monthly
-
ISSN
1006-6772
-
CN
11-3676/TD
Covered by
- CSTPCD
- RCCSE(A+)
- AJ
- EBSCO host
- Ulrichsweb
- JST
- Scopus
Contact us
New Media
-
 Meichuanmei
Meichuanmei -
 Clean Coal Technology
Clean Coal Technology -
 Online Journals
Online Journals








 Submission system
Submission system Copyright agreement
Copyright agreement Instructions for authors
Instructions for authors