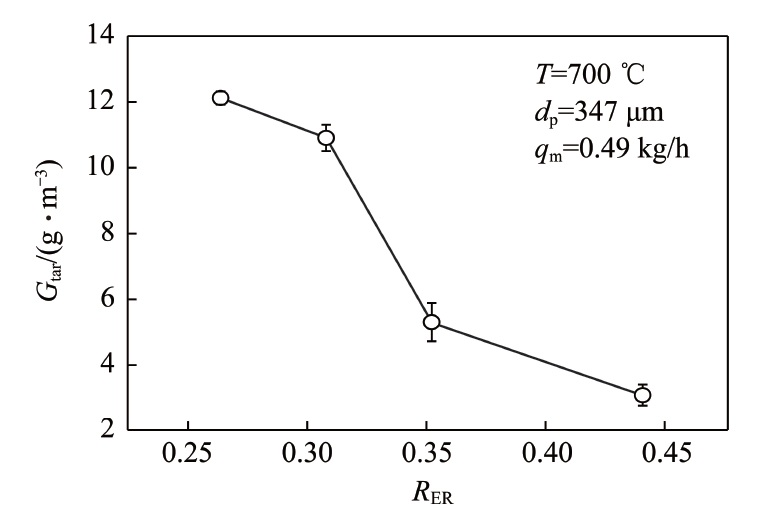
Tar generated during the coal gasification may condense at low temperature,thus blocking the process equipment,leading to the pollution of the equipment,and increasing operating costs. The adjustment of operation parameters based on the tar generation characteristics would be conducive to reduce the original tar emission from a gasifier and reduce the cost of tar removal. In order to obtain the generation characteristics of tar in fluidized bed coal gasification,the effects of parameters such as bed temperature,air equivalent ratio,superficial gas velocity,coal particle size and water content,upon the generation amount of tar in the product gas were studied by fluidized bed reactor. The results show that increasing temperature or air equivalent ratio is beneficial to the decrease of tar mass concentration,but the effects are both limited. When the apparent gas velocity ug in the furnace increases from 0.19 to 0.33 m/s,more intensified contact and mixing between gas and solids improve the effects of heat transfer and mass transfer in the gasifier and promote the thermal decomposition of tar produced. However,as the bubbling fluidization transits to turbulent fluidization,the contact and mixing between gas and solids are no longer significantly enhanced,and the tar mass concentration thus changes little. The small diameters of coal particles can improve the chemical reaction rate and promote the thermal decomposition of tar. However,at a certain fluidization gas velocity,the smaller the gasification feedstocks is,the more it is easily distributed on the bed,which weakens the heat transfer between coals and bed materials,and shortens the residence time of tar in the furnace,leading to the rise of tar mass concentration. The tar mass concentrations in the product gas of coal gasification under different moisture contents have obvious difference. Neither too high nor too low for water content are beneficial to the reduction of tar generation.
Generation characteristics of tar in fluidized bed coal gasification
 2022 No. 04
2022 No. 04
 1064
1064 471
471

Authors:
- DENG Shangzhi
- JIANG Huawei
- LI Weiqiang
- YUAN Ye
- GUO Qingjie
- WANG Cuiping

Unit:
- College of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering,Qingdao University;State Key Laboratory of High-efficiency Utilization of Coal and Green Chemical Engineering,Ningxia University;College of Civil Engineering and Architecture,Shandong University of Science and Technology

Abstract:

Keywords:
- coal gasification
- generation characteristics of tar
- fluidized bed
- superficial gas velocity
- coal particle size
- moisture content
- heat and mass transfer

Citation format:
邓尚致(1995—),男,江西赣州人,硕士研究生。E-mail:shangzhiD@yeah.net
通讯作者:姜华伟(1984—),男,山东荣成人,讲师,博士。E-mail:jianghuawei@tsinghua.org.cn
通讯作者:姜华伟(1984—),男,山东荣成人,讲师,博士。E-mail:jianghuawei@tsinghua.org.cn

Chart:

Articles:
--

Citation format:
--

-
Executive director
China Coal Science and Industry Group Co., Ltd
-
Sponsored by
Coal Science Research Institute Co., Ltd
Coal Industry Clean Coal Engineering
Technology Research Center -
Editor in Chief
XIE Qiang
-
Vice Editor-in-Chief
YU Chang
SHI Yixiang
ZHAO Yongchun
DUAN Linbo
CAO Jingpei
ZENG Jie -
Publication Frequencies
Monthly
-
ISSN
1006-6772
-
CN
11-3676/TD
Covered by
- CSTPCD
- RCCSE(A+)
- AJ
- EBSCO host
- Ulrichsweb
- JST
- Scopus
Contact us
New Media
-
 Meichuanmei
Meichuanmei -
 Clean Coal Technology
Clean Coal Technology -
 Online Journals
Online Journals









 Submission system
Submission system Copyright agreement
Copyright agreement Instructions for authors
Instructions for authors