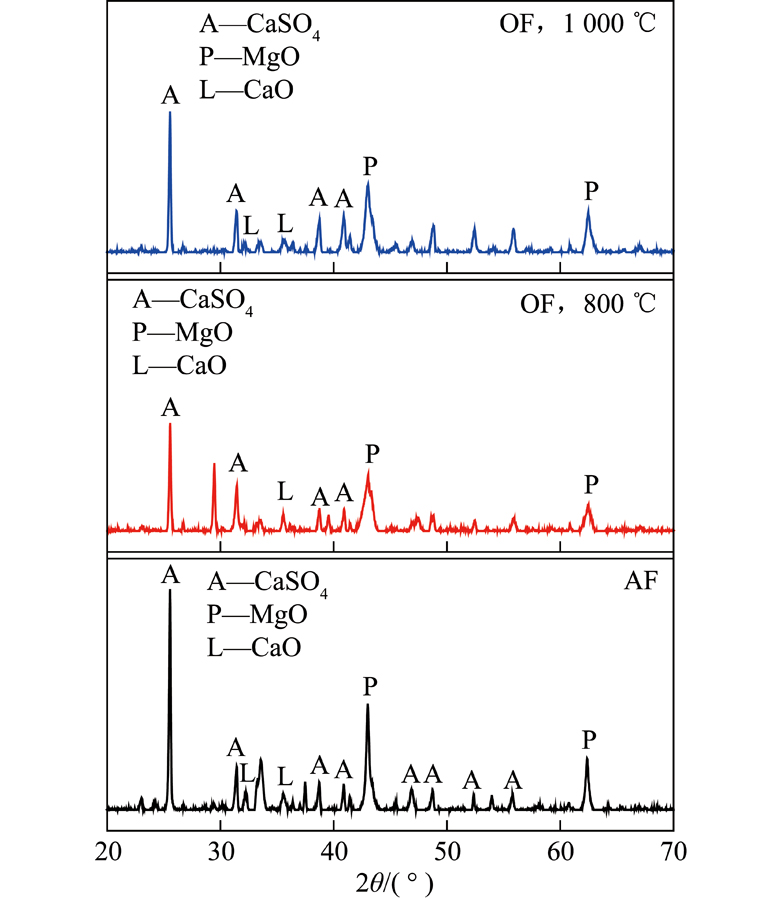
During the oxy-fuel combustion, rich CO2 is produced in flue gas with varied SOx concentration. In this paper, the characteris⁃tics of sulfur retention in fly ash from different coal in oxy-fuel combustion was studied. The SOx absorption in fly ashes of six coals wastested on the high-temperature drop-tube furnace, in which the flue gas atmosphere set for oxy-fuel or air burning. The influencing fac⁃tors were analyzed. The results show that the sulfur retention amount is very low in bituminous coal ash, which is related to the lack of al⁃kaline earth metal (Ca, Mg) in bituminous coal ash. However, the sulfur retention of lignite ash is significant. The fixed sulfur efficiencyis about 43% for lignite ash after air-firing, as compared with 60% after its oxy-fuel combustion. The sulfur absorption rate is much high⁃er in oxy-fuel flue gas in 1 000 ℃ rather than in 800 ℃ . The temperature window and reaction effect of fly ash sulfur fixation are consist⁃ent with the reaction of SO2 oxidation to SO3. Some alkaline earth metals have combined with Si or Al, etc., and these alkaline earth met⁃als do not have sulfur fixation activity. SO3 formation is effected by both catalytic effect of Fe2O3 and the sulfur-retention behavior in ash.Through both oxy-fuel combustion and dry scrubbing of Ca sorbent added together, it is promising to control SOx emission deeply in furnace.
Experiment of sulfur retention characteristics of fly ash in pulverizedcoal oxy-fuel-firing flue gas
 2023 No. 08
2023 No. 08
 391
391 324
324

Authors:
- ZHANG Jian
- CAO Ruijie

Unit:
- School of Environment and Architecture Engineering,University of Shanghai for Science and Technology
- Shanghai Institute for Design and Research on Environmental Engineering

Abstract:

Keywords:
- oxy-fuel combustion
- lignite
- fly ash
- sulfur retention
- sulfur oxide

Citation format:
张健(1978—),男,山东济南人,讲师,博士。E-mail:jzhang66@163.com

Chart:

Articles:
--

Citation format:
ZHANG Jian,CAO Ruijie. Experiment of sulfur retention characteristics of fly ash in pulverized coal oxy - fuel - firingflue gas[J].Clean Coal Technology,2023,29(8):102-108.

-
Executive director
China Coal Science and Industry Group Co., Ltd
-
Sponsored by
Coal Science Research Institute Co., Ltd
Coal Industry Clean Coal Engineering
Technology Research Center -
Editor in Chief
XIE Qiang
-
Vice Editor-in-Chief
YU Chang
SHI Yixiang
ZHAO Yongchun
DUAN Linbo
CAO Jingpei
ZENG Jie -
Publication Frequencies
Monthly
-
ISSN
1006-6772
-
CN
11-3676/TD
Covered by
- CSTPCD
- RCCSE(A+)
- AJ
- EBSCO host
- Ulrichsweb
- JST
- Scopus
Contact us
New Media
-
 Meichuanmei
Meichuanmei -
 Clean Coal Technology
Clean Coal Technology -
 Online Journals
Online Journals









 Submission system
Submission system Copyright agreement
Copyright agreement Instructions for authors
Instructions for authors