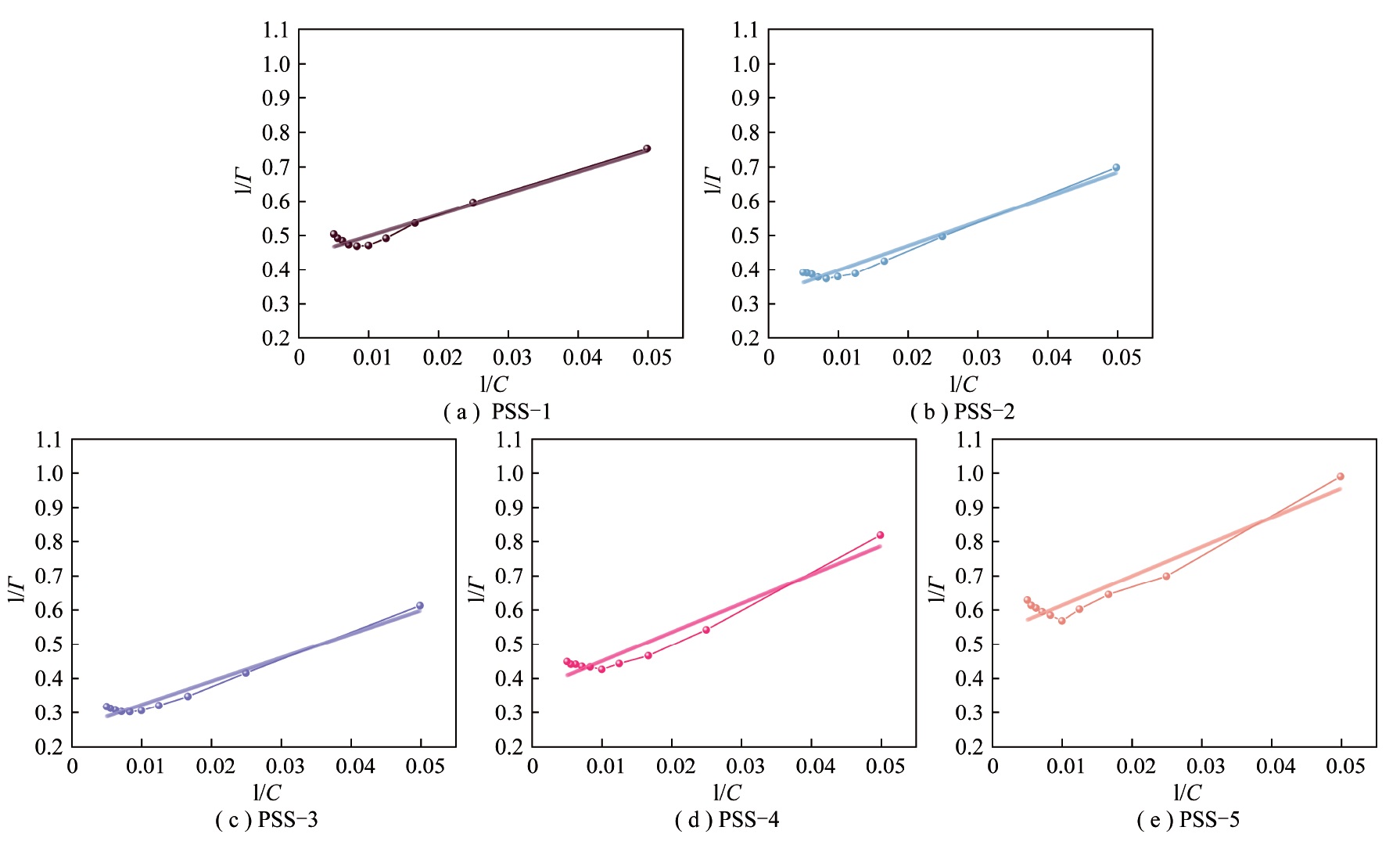
To improve the status quo of low slurry formation concentration and poor slurry performance of non-stick coal, Herein, Shenhua non-stick coal (SNC) was used as the object of study, and five kinds of sodium polystyrene sulfonate (PSS) dispersants with different lipophilic strengths were selected. The mechanism of the effect of the dispersant lipophilic groups on the slurry formation of SNC was investigated by examining the constitutive relationships between the strength of PSS lipophilic groups and the rheological properties, stability performance, wetting performance and adsorption behavior of SNC coal-water slurry. The results show that the strength of the lipophilic groups of PSS dispersants significantly affects the stability, rheology and apparent viscosity of the non-stick coal slurry. The longer lipophilic chain segments, the increases cross-linking between molecules and the larger spatial potential resistance formed make the slurry more stable. However, the apparent viscosity and rheology of coal-water slurry will be extremely high when the polymerization degree of PSS is 187 because the adsorption amount of dispersant molecules on the coal surface and its adsorption constant KL value increase and then decrease with the increase of PSS polymerization degree. SNC particle surface, which in turn forms uniform water molecule adsorption sites on the coal particle surface and promotes the formation of a uniformly textured hydration film.The SNC coal water slurry prepares with the dispersant content of 0.6% of dry coal powder and the slurry concentration of more than 61% has better slurry performance.
Effect of lipophilic groups of PSS dispersant on the slurry formation characteristics and surface adsorption behavior of non-stick coal
 2023 No. 06
2023 No. 06
 678
678 246
246

Authors:
- YE Zefu
- MENG Xianliang
- WU Guoguang

Unit:
- Shanxi Gemeng US-China Clean Energy R&D Center Co.,Ltd.,
- School of Chemical Engineering & Technology,China University of Mining & Technology

Abstract:

Keywords:
- PSS dispersant
- lipophilic group
- adsorption behavior
- coal water slurry
- slurry properties

Citation format:
叶泽甫(1980—),男,河南开封人,高级工程师,硕士。E-mail:yezefu2000@163.com

Chart:

Articles:
--

Citation format:
YE Zefu,MENG Xianliang,WU Guoguang.Effect of lipophilic groups of PSS dispersant on the slurry formation characteristics and surface adsorption behavior of non-stick coal[J].Clean Coal Technology,2023,29(6):180-188.

-
Executive director
China Coal Science and Industry Group Co., Ltd
-
Sponsored by
Coal Science Research Institute Co., Ltd
Coal Industry Clean Coal Engineering
Technology Research Center -
Editor in Chief
XIE Qiang
-
Vice Editor-in-Chief
YU Chang
SHI Yixiang
ZHAO Yongchun
DUAN Linbo
CAO Jingpei
ZENG Jie -
Publication Frequencies
Monthly
-
ISSN
1006-6772
-
CN
11-3676/TD
Covered by
- CSTPCD
- RCCSE(A+)
- AJ
- EBSCO host
- Ulrichsweb
- JST
- Scopus
Contact us
New Media
-
 Meichuanmei
Meichuanmei -
 Clean Coal Technology
Clean Coal Technology -
 Online Journals
Online Journals











 Submission system
Submission system Copyright agreement
Copyright agreement Instructions for authors
Instructions for authors