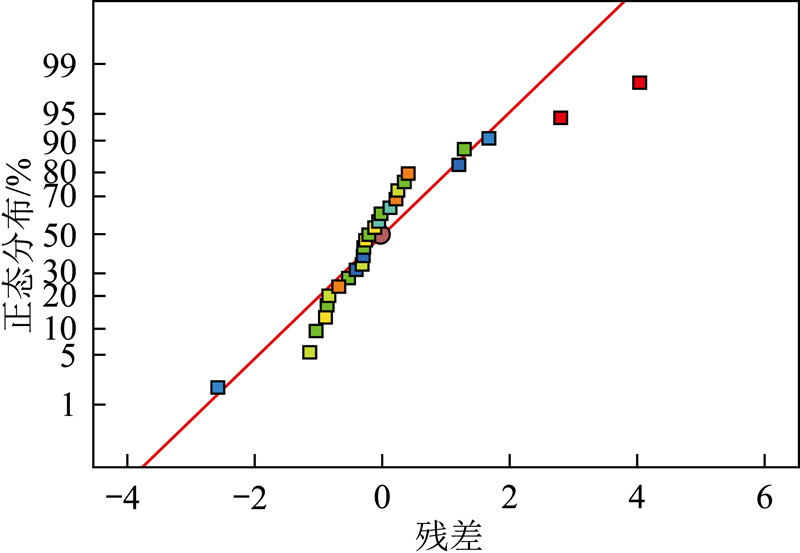
The kaolin content of gangue in the Heidaigou ming area is as high as 70%. Herein, from the perspective of comprehensive utilization of coal resources, in order to improve the calcination whiteness of coal-derived kaolin, a method of centrifugal for separation was used to remove the chromogenic impurities with high-density. To achieve this, this work performed orthogonal design by Design Expert and adopted the Box-Behnken model. Consequently, the influence of centrifugal speed, feeding rate, feeding concentration and feeding time on the calcination whiteness and concentrate yield was explored and the quadratic equation relationship model was fitted. Further, the response surface plots of calcination whiteness and concentrate yield with significant factors were given. It was found that the whiteness of calcination was mainly affected by the centrifugal speed. With the increase of the rotation speed of the drum, the whiteness of the calcination first increased and then decreased. The yield of concentrate was mainly affected by the feeding time. With the extension of feeding time, the yield of concentrate increased linearly. Finally, combined with the simulation results of Design Expert, the optimal centrifugal separation conditions were analyzed and explored. When the centrifugal speed is 800 r/min, feeding rate is 8.4 L/min, feeding concentration is 20%, and feeding time is 100 s, the optimal calcination whiteness (78.80%) and concentrate yield (86.31%) of kaolin can be obtained.
Experimental study on centrifugal separation and calcinationof coal-derived kaolin by Design Expert
 2023 No. 05
2023 No. 05
 441
441 231
231

Authors:
- DU Pengtao
- ZHAO Shiyong
- LIANG Xiao

Unit:
- School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering,Xi′an University of Science and Technology
- Xi′an Northwest Research Institute of Non-ferrous Geology Co.,Ltd.,

Abstract:

Citation format:
杜鹏涛(1995—),男,陕西西安人,硕士研究生。E-mail:744408526 @qq.com

Chart:

Articles:
--

Citation format:
DU Pengtao,ZHAO Shiyong,LIANG Xiao.Experimental study on premixed ammonia/air swirl combustion assisted by dielectric barrier discharge[J].Clean Coal Technology,2023,29(5):124-132.

-
Executive director
China Coal Science and Industry Group Co., Ltd
-
Sponsored by
Coal Science Research Institute Co., Ltd
Coal Industry Clean Coal Engineering
Technology Research Center -
Editor in Chief
XIE Qiang
-
Vice Editor-in-Chief
YU Chang
SHI Yixiang
ZHAO Yongchun
DUAN Linbo
CAO Jingpei
ZENG Jie -
Publication Frequencies
Monthly
-
ISSN
1006-6772
-
CN
11-3676/TD
Covered by
- CSTPCD
- RCCSE(A+)
- AJ
- EBSCO host
- Ulrichsweb
- JST
- Scopus
Contact us
New Media
-
 Meichuanmei
Meichuanmei -
 Clean Coal Technology
Clean Coal Technology -
 Online Journals
Online Journals






 Submission system
Submission system Copyright agreement
Copyright agreement Instructions for authors
Instructions for authors