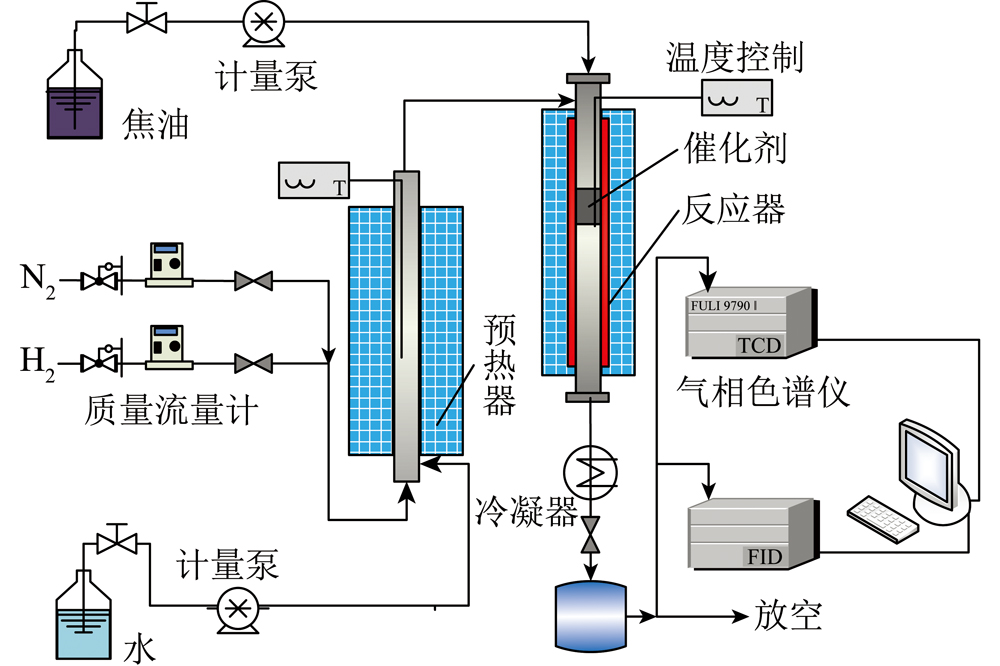
The coal fast pyrolysis/circulating fluidized bed combustion/catalytic reactor coupled fractionation conversion process is easy to operate and maintain, with significant economic benefits, which is one of the effective ways to achieve clean and efficient utilization of coal resources. However, due to the poor tar quality and high pollution element content produced by the rapid coal pyrolysis process, the catalyst is frequently deactivated and regenerated. Therefore, a cheap and efficient non regenerative catalyst has been prepared in this paper. The effects of calcination temperature and modification method of catalyst on the catalytic cracking characteristics of coal tar were investigated in a fixed bed catalytic reactor with low-temperature coal tar as raw material and natural dolomite as research object. The 1% Ni/2%Fe dolomite catalyst was prepared under the optimum preparation conditions, and the effect of reaction temperature on the catalytic cracking of coal tar was investigated. The results show that with the increase of calcination temperature, the main components of dolomite, such as CaCO3 and MgCO3 is promoted to convert into CaO and MgO active substances, and the activity of natural dolomite catalyst gradually increases and tends to be stable, with the optimal calcination temperature of 750 ℃. The cracking of tar is not promoted by introducing Fe alone, but the catalytic activity of natural dolomite catalyst is significantly improved by introducing Ni and Fe at the same time. The best modification method is 1% Ni/2% Fe dolomite. The introduction of Fe as a promoter protects the sulfur poisoning deactivation of the active component Ni, while the introduction of Ni and Fe alleviates the sintering phenomenon of the catalyst. Fe can be used as an auxiliary agent to slow down the generation of carbon deposits in the catalytic process. The dolomite catalyst modified by Ni promotes the cracking of aliphatic compounds and sulfur-containing compounds. Indene and naphthalene compounds do not undergo cracking reactions, but products such as hydroindene and hydronaphthalene appear.
Preparation and catalytic cracking characteristics of coal tar cracking catalyst
 2023 No. 02
2023 No. 02
 562
562 306
306

Authors:
- MENG Dechang
- ZHAO Yuan
- ZHANG Yaqing
- JIAO Tiantian
- GU Xiaohui
- WANG Guangyao
- LIANG Peng

Unit:
- Beijing Research Institute of Coal Chemistry,China Coal Research Institute Co.

Abstract:

Keywords:
- dolomite
- Nickel based catalyst
- catalyst preparation
- coal tar
- catalytic cracking

Citation format:
孟德昌(1995—),男,山东菏泽人,实习研究员,硕士。E-mail:meng10910@126.com

Chart:

Articles:
--

Citation format:
--

-
Executive director
China Coal Science and Industry Group Co., Ltd
-
Sponsored by
Coal Science Research Institute Co., Ltd
Coal Industry Clean Coal Engineering
Technology Research Center -
Editor in Chief
XIE Qiang
-
Vice Editor-in-Chief
YU Chang
SHI Yixiang
ZHAO Yongchun
DUAN Linbo
CAO Jingpei
ZENG Jie -
Publication Frequencies
Monthly
-
ISSN
1006-6772
-
CN
11-3676/TD
Covered by
- CSTPCD
- RCCSE(A+)
- AJ
- EBSCO host
- Ulrichsweb
- JST
- Scopus
Contact us
New Media
-
 Meichuanmei
Meichuanmei -
 Clean Coal Technology
Clean Coal Technology -
 Online Journals
Online Journals










 Submission system
Submission system Copyright agreement
Copyright agreement Instructions for authors
Instructions for authors