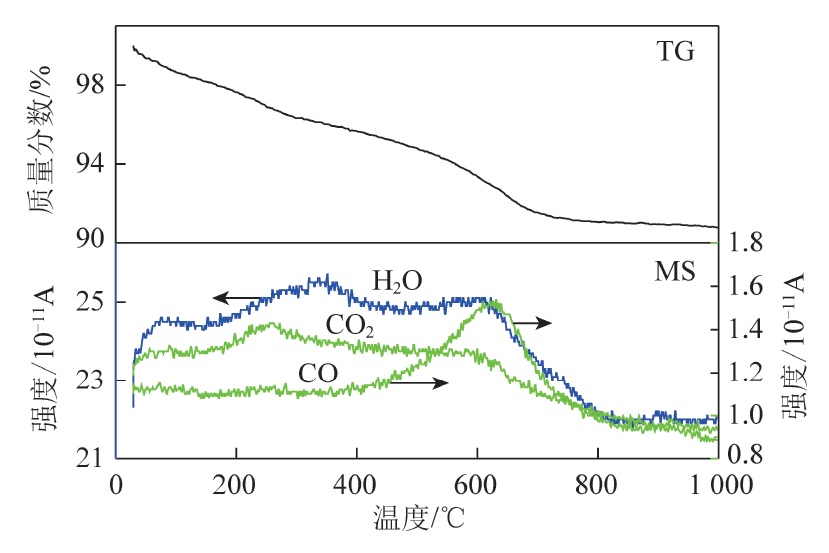
Supercapacitor is a new type of energy storage device,and electrode material as its key component has been attracting much attention,among which the modification treatment of electrode material is crucial for the research of high-performance supercapacitor.Coal-based capacitive carbon with high specific surface area (2 586 m2/g) was prepared with using Hebei anthracite coal as the precursor,KOH as the activator,alkali to coal mass ratio of 2∶1 and activation temperature of 800 ℃. The evolution of microstructure and surface chemistry of the capacitance carbon during hydrothermal reduction at different temperatures (600-1 000 ℃) and their effects on electrochemical properties were investigated by using coal-based capacitance carbon as raw material. The results show that with the increase of hydrothermal reduction temperature,the specific surface area of the samples first slightly increases and then gradually decreases,and the mesoporosity increases to different degrees compared with the original coal-based capacitive carbon. Among them,the samples obtained by hydrothermal reduction treatment at 700 ℃ have lower oxygen content (0.35%),stronger electrical conductivity,better wettability with organic electrolyte and higher degree of defects,and the electrochemical properties has been significantly improved:higher specific capacitance (179 F/g at 0.5 A/g current density),energy density (33.36 Wh/kg),power density (1 014.75 W/kg),multiplicative performance (58.7% capacitance retention at 5 A/g current density),and cycling stability (82% capacitance retention at 5 000 cycles). For coal-based capacitive carbon,hydrothermal reduction is a good modification treatment.
Effect of modification on structure and electrochemical properties of coal based activated carbon
 2022 No. 04
2022 No. 04
 1146
1146 773
773

Authors:
- ZHANG Zhaohua
- WANG Qian
- ZHANG Buqin
- ZHANG Fengmei
- ZHANG Chuanxiang
- HUANG Guangxu
- XING Baolin

Unit:
- College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering,Henan Polytechnic University;Jizhong Energy Fengfeng Group Co.,Ltd.,

Abstract:

Keywords:
- supercapacitors
- coal-based activated carbon
- modification
- oxygen-containing functional group
- electrochemical propeties

Citation format:
张兆华(1994—),男,河南焦作人,硕士研究生。E-mail:zzh15239168493@163.com
通讯作者:张传祥(1970—),男,河南濮阳人,教授,博士生导师,博士。E-mail:zcx223@163.com
通讯作者:张传祥(1970—),男,河南濮阳人,教授,博士生导师,博士。E-mail:zcx223@163.com

Chart:

Articles:
--

Citation format:
--

-
Executive director
China Coal Science and Industry Group Co., Ltd
-
Sponsored by
Coal Science Research Institute Co., Ltd
Coal Industry Clean Coal Engineering
Technology Research Center -
Editor in Chief
XIE Qiang
-
Vice Editor-in-Chief
YU Chang
SHI Yixiang
ZHAO Yongchun
DUAN Linbo
CAO Jingpei
ZENG Jie -
Publication Frequencies
Monthly
-
ISSN
1006-6772
-
CN
11-3676/TD
Covered by
- CSTPCD
- RCCSE(A+)
- AJ
- EBSCO host
- Ulrichsweb
- JST
- Scopus
Contact us
New Media
-
 Meichuanmei
Meichuanmei -
 Clean Coal Technology
Clean Coal Technology -
 Online Journals
Online Journals









 Submission system
Submission system Copyright agreement
Copyright agreement Instructions for authors
Instructions for authors