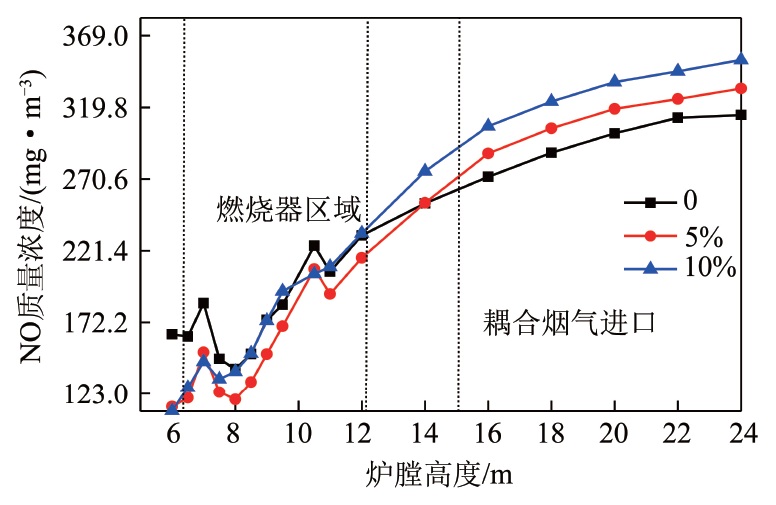
The technology of coal fired coupled waste incineration power generation can make full use of the existing coal fired units and environmental protection facilities,co-processing waste,reduce waste-to-energy costs,improve the scale of waste treatment,and reduce the coal consumption of coal fired power,increase the proportion of non-fossil energy utilization. At present,there are three coupling modes in coal-fired coupled waste incineration power generation technology:flue gas side coupling,fuel side coupling and steam side coupling. In order to study the coupled incineration power generation technology,a coupling transformation scheme based on a 220 t/h tangentially pulverized coal boiler was proposed. Among them,the pulverized coal in the pulverized coal boiler of the system before transformation is burned alone,accounting for 100% of the total input calorific,and after the transformation,the waste calorific replaces 5% and 10% of the total input calorific,while the pulverized coal accounts for 95% and 90% of the total input calorific. The combustion conditions before and after the transformation were analyzed by Fluent simulated. The results show that the flue gas side coupling transformation will make the boiler flow field more complex,and the higher the proportion of waste replacing coal calorific is,the more obvious the impact is;the average temperature of the furnace section is affected by the coupled flue gas volume. The average flue gas temperature at the outlet section increases with the increase of the calorific ratio of waste to coal. The flue gas outlet temperature is 1 366.9 K when pulverized coal is burned alone before the transformation. After the transformation,the average flue gas outlet temperature of the 5% waste to coal calorific ratio system increases to 1 409.9 K,and the average flue gas outlet temperature increases to 1 420.1 K when 10%;the NO concentration at the furnace outlet increases with the increase of the calorific proportion of waste replacing coal. Compared with the separate combustion of pulverized coal before the transformation,the NO emission concentration of the 5% waste replacing coal calorific proportion system after the transformation increases by 6.3% and 13.0% when the proportion system is 10%;the SO2 concentration at the furnace outlet decreases with the increase of the calorific proportion of waste replacing coal. Compared with that before the transformation,the SO2 concentration of the 5% waste replacing coal calorific proportion system after the transformation decreases by 40.9%,and that of the 10% proportion system decreases by 41.4%.
Numerical simulation of flue gas side coupled municipal solidwaste incineration in a 220 t/h boiler
 2022 No. 03
2022 No. 03
 573
573 494
494

Authors:
- SHI Bingquan
- SHI Mingzhe
- ZHANG Rui

Unit:
- School of Energy and Power Engineering,Nanjing University of Science and Technology;Zibo Chenyue Baoshan Environmental Protection Technology Co.,Ltd.,

Abstract:

Keywords:
- flue gas side coupling
- municipal solid waste incineration
- coal-fired boiler
- coal-fired calorific

Citation format:
史兵权(1995—),男,河南周口人,硕士研究生。E-mail:118108010867@njust.edu.cn
通讯作者:张睿(1986—),男,江苏徐州人,副教授,博士。E-mail:zhangrui@njust.edu.cn
通讯作者:张睿(1986—),男,江苏徐州人,副教授,博士。E-mail:zhangrui@njust.edu.cn

Chart:

Articles:
--

Citation format:
--

-
Executive director
China Coal Science and Industry Group Co., Ltd
-
Sponsored by
Coal Science Research Institute Co., Ltd
Coal Industry Clean Coal Engineering
Technology Research Center -
Editor in Chief
XIE Qiang
-
Vice Editor-in-Chief
YU Chang
SHI Yixiang
ZHAO Yongchun
DUAN Linbo
CAO Jingpei
ZENG Jie -
Publication Frequencies
Monthly
-
ISSN
1006-6772
-
CN
11-3676/TD
Covered by
- CSTPCD
- RCCSE(A+)
- AJ
- EBSCO host
- Ulrichsweb
- JST
- Scopus
Contact us
New Media
-
 Meichuanmei
Meichuanmei -
 Clean Coal Technology
Clean Coal Technology -
 Online Journals
Online Journals















 Submission system
Submission system Copyright agreement
Copyright agreement Instructions for authors
Instructions for authors